Prepare yourself for crypto security
It’s important to stay safe with crypto security. There are also tons of malicious activities because there is a lot of real money involved. Criminals are extremely creative by using various techniques to empty your wallet. Think of a malicious smart contract that either lets you sell with an incredibly high fee or does not let you sell at all. This means that your money is lost.
Good practices and types of scams
On this page we will tell you about types of scams, but also about good practices which really help you stay safer out there. Even though we are writing this page with a 10+ years experience in the space, every year we are confronted with new types of scams and therefore can’t guarantee with the below tips that you stay 100% safe. But we’ll do our best and we hope you do so to!
Better safe than sorry
Here you will find all the best tips and tricks to ensure you are not an easy target!
We’ve summarized good practices to stay safe out there.
01
Never ever back up your seed phrase digitally. It’s better to stamp it in metal and keep it in a safe.
02
Always verify smart contracts and website links before interacting or downloading.
03
Use cold storage for the long-term safety of your digital money. More about cold storage.
04
Trust no one in this business, not even your own family. Just don’t ever talk about it!
Crypto security: which types of Scams are there?
To get a good understanding on how to stay safe, it is important to learn what type of scams are out there. It is impossible to keep this list up to date due to the many novelties are found each day, but we’ll do our best!
Phishing Scams:
Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information, such as private keys or login credentials, by posing as a trustworthy entity through fake websites or communication. The goal is to obtain your login credentials or private keys to steal your funds associated with that wallet. There are many forms of phishing but the most known ones are e-mail phishing (malicious links in the email), clone phishing (clone software or cloned webpage) and pop-up phishing (pop-ups on trustworthy websites that direct you to malicious software).
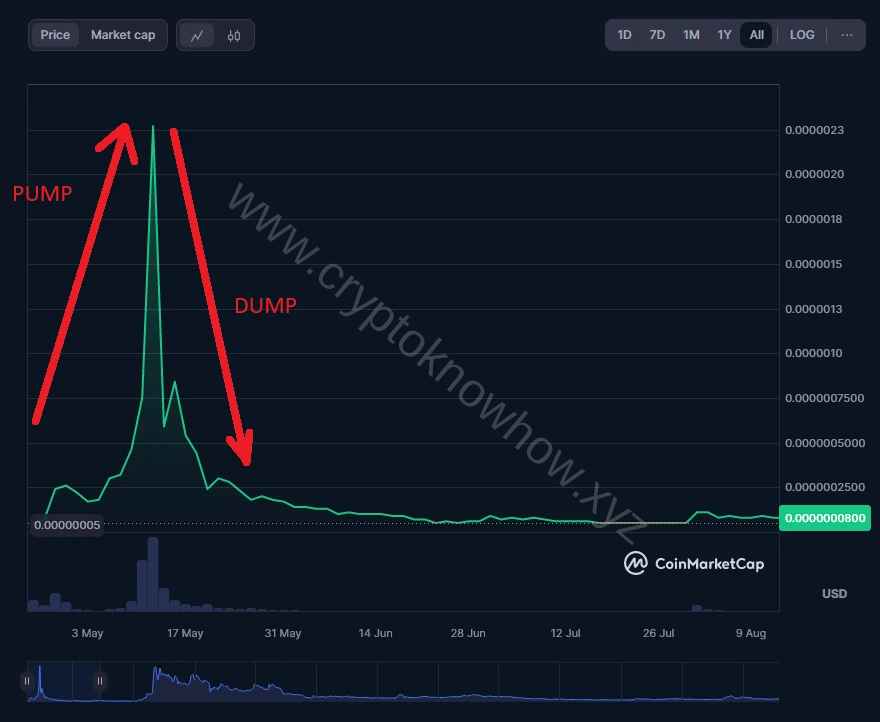
Pump and Dump Schemes:
Inflating the price of a low-volume cryptocurrency through coordinated buying (pump), followed by rapid selling (dump) to capitalize on the price surge, leaving unsuspecting investors with losses. The following graph shows how someone ‘pumped’ and ‘dumped’ a token (the specific name is not relevant):
Fake ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings):
Deceptive fundraising schemes where fraudsters create and promote fake ICOs/ This leads non-suspecting investors to use their funds in exchange for non-existent tokens.
Exit Scams:
An exit scam occurs when the creators or operators of a cryptocurrency project, such as an ICO or a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, abruptly abandon the project after raising funds from investors. The individuals behind the project vanish, leaving contributors with no recourse and a project that never materializes as promised.
Rug Pulls:
A rug pull is a specific type of scam that often occurs in the context of decentralized finance (DeFi) projects or token launches. A rug pull happens when the creators of a project suddenly and deliberately drain the liquidity or funds from the project/ This leaves you and I worthless or significantly devalued tokens.
A very infamous rug pull is the token ‘SQUID’ after the Netflix series of Squidgame. In 2021 it was launched and raised approx $ 3.5 Million, after which the developers ran with the funds. Another example is AnubisDAO, which shows that DAOs are not immune to rug pulls either!
Fake Exchanges:
Scammers create fraudulent cryptocurrency exchanges or copy existing ones that appear legitimate but exist solely to steal user funds. BOOKMARK your websites you deal with to prevent googling the website and accidentally clicking on a malicious ad instead of the service you are needing.
Impersonation or Social Engineering:
Criminals can easily pose as influential figures or projects on social media platforms to deceive users into sending cryptocurrencies. Discord scams belong to this category as well. Discord scams happen when a project gets hacked and a user places fake links with the promise of an airdrop and X $ of that token. Once you click the malicious link and connect your wallet, you will be emptied.
Cryptojacking:
Cryptojacking is a form of scamming in which malicious actors secretly use the computing power of your and my PC to mine cryptocurrencies without our knowledge or consent. This often involves infecting websites, applications, or computers with malware that uses the our devices its processing power to mine cryptocurrencies for the benefit of the attacker.
Fake Wallets:
Scammers design fake wallets as deceptive applications or services to mimic legitimate cryptocurrency wallets and steal our private keys or funds. These fraudulent wallets often present themselves as trustworthy and user-friendly options, encouraging us to download and use them for storing our cryptocurrencies. Once installed, these fake wallets may compromise the security of private keys, enabling scammers to gain unauthorized access to our funds.
Cloud Mining Scams:
A cloud mining scam happens when they falsely promise us remote cryptocurrency mining with high returns. They indeed let us mine, however, the operators will vanish without delivering on the promised rewards and keep everything for themselves. Caution and thorough research are crucial to avoid becoming a victim to such deceptive schemes.
Ponzi Schemes:
A single operator or organization attracts investors by promising high returns. Using the capital from new investors, the scheme pays returns to existing investors, creating the illusion of profitability. The scheme relies on a continuous influx of new investors to sustain payouts, and it inevitably collapses when the flow of new investments slows down. This can go well for a very long time, until now new investors come anymore. Then literally S*#& hits the fan.
Multilevel Marketing (MLM) Schemes:
MLM schemes involve a network of participants who can earn commissions not only for their direct sales but also for recruiting new members into the network. Participants may be required to purchase products or pay an entry fee. Some illegal MLMs share characteristics with pyramid/ponzi schemes, where recruitment becomes the primary focus, and unsustainable structures lead to losses for the users of the platform.
Address Poisoning
Address poisoning in crypto involves malicious actors providing false wallet addresses to users, typically during transactions or fund transfers to the non-suspecting individual. This scam works because unsuspecting users trust the provided address, believing it belongs to the intended recipient, leading to funds being sent to the scammer his/her wallet instead of the intended destination. To prevent this, whitelist your own addresses in every service available and only use these whitelisted addresses.
Good practices for crypto security:
- Use Cold Storage for bigger savings in crypto;
- Don’t leave big amounts on any exchange, if they go bankrupt or magically disappear, you won’t lose too much;
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) wallets (Metamask for example) are for free. If you interact with ‘new’ things, use new wallets. If you accidentally sign a malicious smart contract, you don’t lose everything you have;
- Update your wallet software always to the latest version to make sure you benefit from the latest security updates;
- Use 2FA;
- NEVER EVER backup your seed phrase of ANY wallet online. Always OFFLINE. Preferably stamped in metal or kept secure in a lock-box/safe to prevent fire or water damage;
- If you are using cold storage, NEVER EVER fill out your seed phrase in any online interface. Literally EVERY online interface for your cold storage asking for your seed phrase is a scam attempt. Criminals use Google Ads on the most popular cold storage to fool you into downloading their fake (clone) software;
- Revoke access to contracts you have interacted with. You can do this on block explorers. This prevents unauthorized access at a later moment in time;
- Don’t trust anyone!! Don’t talk about crypto with family and friends, it can backfire in a lot of ways (begging, trust issues, stealing, jealousy, etc.);
- Work with whitelisted addresses. IN every platform you get an option to work with this, it prevents copy pasting the wrong address in the ‘ to ‘ field for transfers. Criminals use various techniques and having whitelisted addresses in the platforms gives them fewer options!
- Use unique and strong passwords for everything, passwords could be saved in a password manager, unlike your seed phrase (use password generation in your password manager for 20+ character passwords, avoids being brute-forced);
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for transactions;
- If you do have the option, use a dedicated notebook or PC for crypto only and don’t interact with anything else online with that device;
- Use advanced security tools to get to know everything about a certain crypto. Only this way you can make better informed decisions:

Crypto security: How to report scams?
If you did get scammed, usually your funds are gone. However, there are ways to report certain illegal activities which will lead to results certain addresses will be marked as scammers’ addresses. Sometimes, they can even retrace the scammer if they transfer funds through a CEX. Only do this if you have proof and are certain.

